Basic concepts of orders and work orders:
An order is a demand placed by a customer on us. Usually the order only includes the finished product for sale.
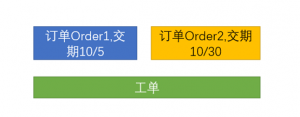
Work orders are called production orders in some ERPs and are internal production task orders issued to complete production.
Work orders are issued based on orders, but there is not necessarily a one-to-one correspondence.
For example: the customer places a long-term order with a large quantity, but the work order cannot be too large and needs to be split according to the production cycle. A work order can be opened for weekly output.
Or multiple small work orders can be merged into one work order to simplify production management.