PlanMateAPS machining solutions
The mechanical processing industry has complex procedures and numerous equipment, making it difficult to formulate and modify production plans. The PlanMateAPS automatic production scheduling system provides production planning and scheduling solutions in this industry, helping companies achieve rapid scheduling, equipment optimization, and on-time delivery, thereby winning the market and customers.
Industry characteristics:
The mechanical processing industry is characterized by a wide variety of equipment, each product needs to go through multiple processes, and the processes of each product are crisscrossed. Because the process is complex, the current manual scheduling method can usually only schedule plans for the next 24-48 hours, and planners often work in scheduling mode rather than planning mode, making it more difficult to modify the plan when the plan changes. It is normal to be unable to estimate the delivery date, fail to deliver on time, and have chaotic plans. This article introduces PlanMatAPS’s automatic production scheduling solution to confused companies.
Program Statistics:
This example includes 964 orders, 9397 in total. The planning time is about 5 weeks, and there are a total of 190 pieces of equipment of various types. Scheduled run time is 2 minutes.
The interface after scheduling is as follows:
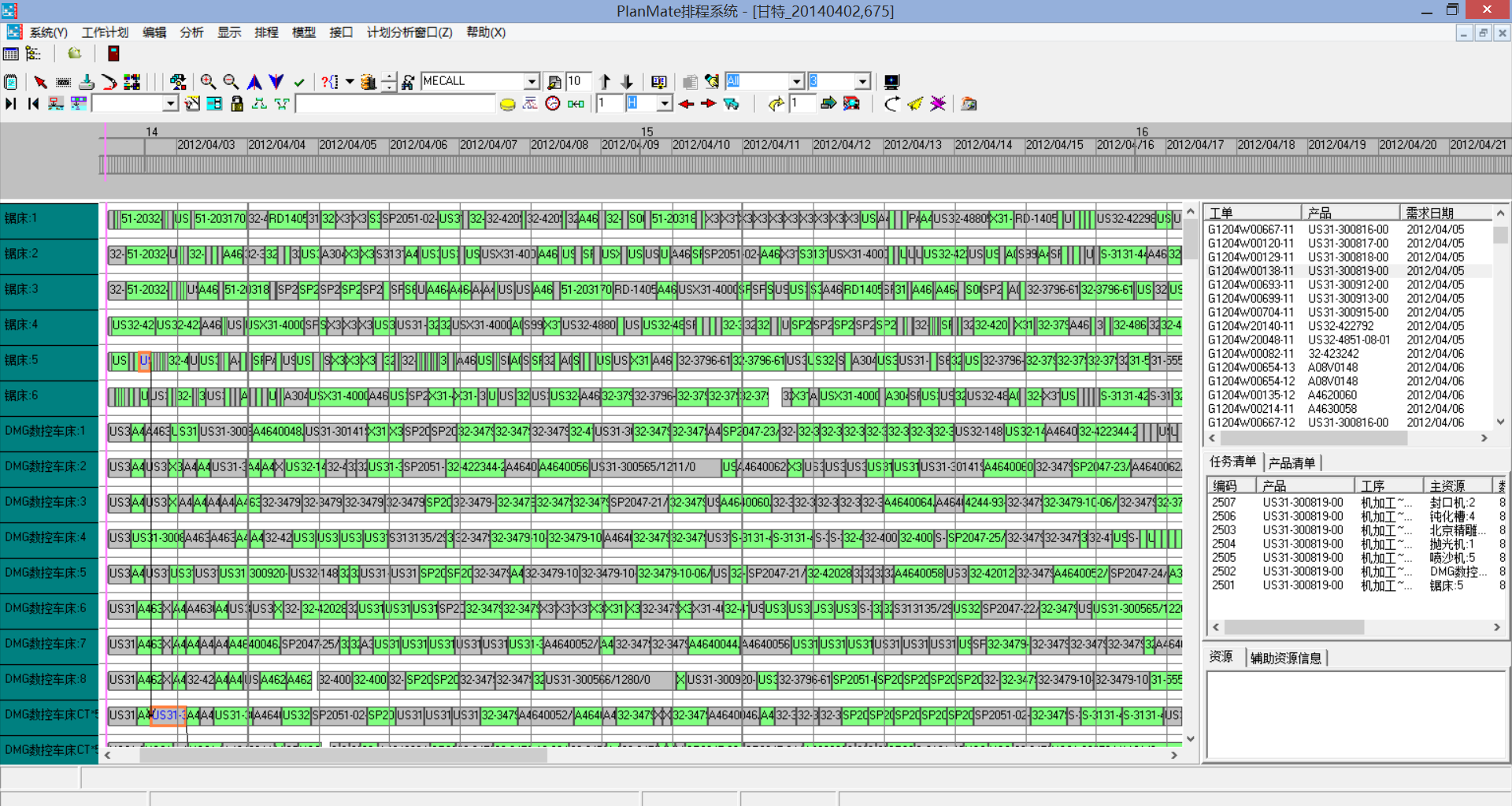
basic concept :
1. PlanMatAPS uses the Gantt chart as the main interface for displaying and operating production plans. Under this interface, users can run schedules, view and analyze plans, and modify plans;
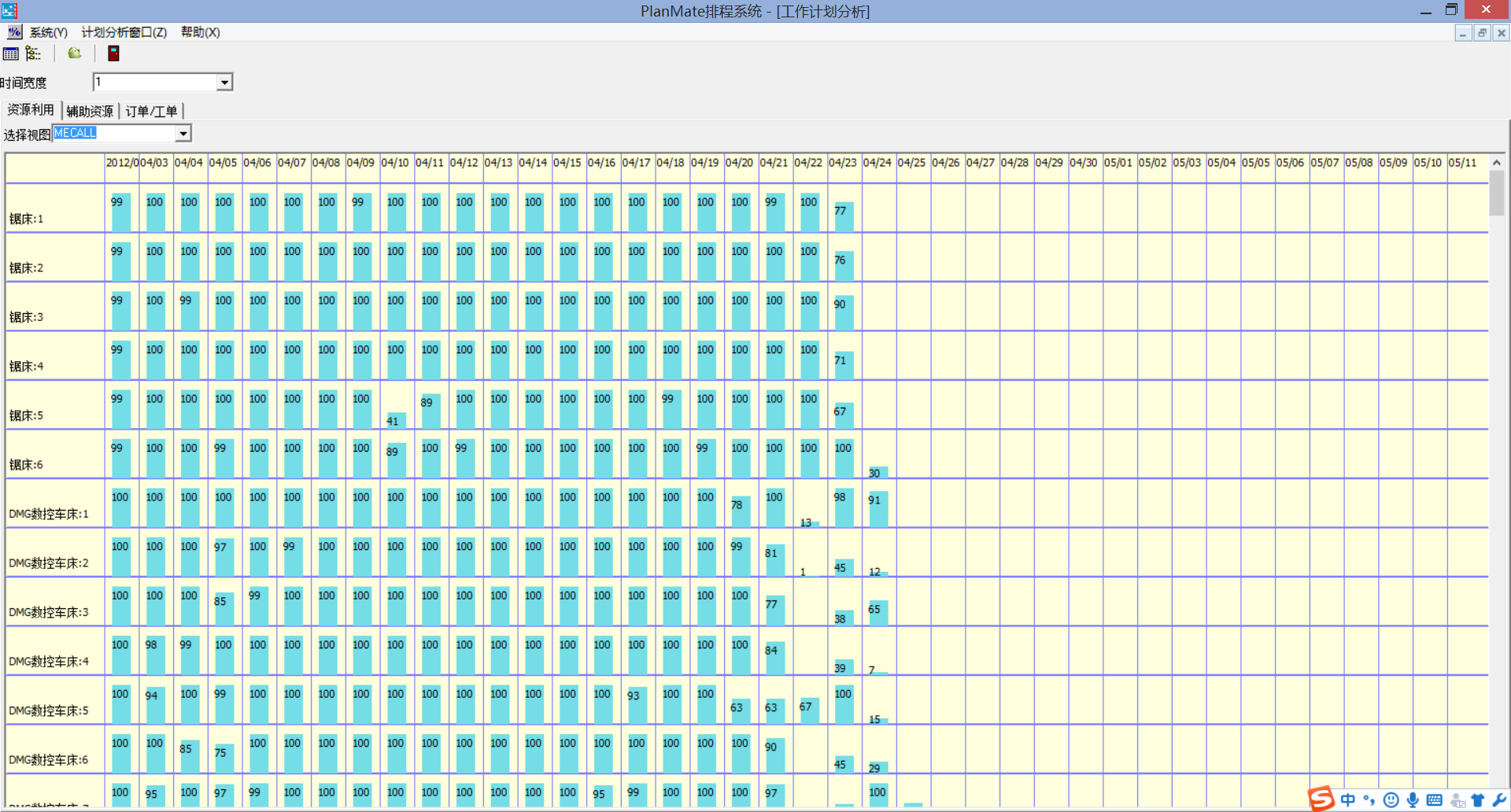
2. In the production plan Gantt chart, the horizontal axis is time, and the units are weeks, days, hours, and minutes. The vertical axis is equipment. Each small rectangle is a production task. PlanMateAPS running time unit is extremely accurate;
3. The product production model mainly includes: BOM, all production processes that the product needs to go through, the machine equipment and cycle time allowed to be used in each process, and the auxiliary resources (molds, fixtures, workers, etc.) to be used in the product process;
4. There are time constraints between processes. Buffering methods and parameters need to be defined in the model, and each product process is defined separately. It can be defined by time or quantity per transfer, and the number of products that the transfer container can reload each time, the required buffer time, etc. must also be considered;
5. The relationship between processes is divided into: a) ES: the previous process is completely completed, and the process can only start after the isolation period; b) EE: there is partial time overlap between the previous process and the subsequent process;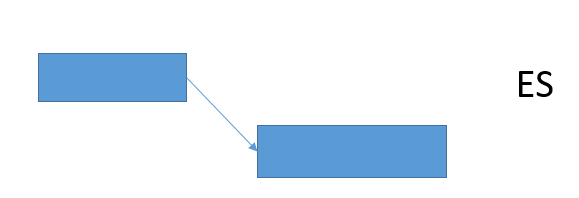
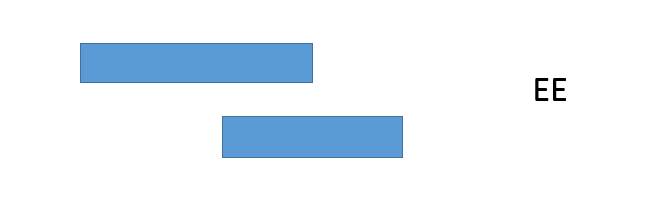
6. Some processes require a long isolation period, such as heating and baking, glue spraying, etc., or you need to wait for quality inspection before production.
7. When work orders are not split (the working time is short), each work order will generate a task after going through a process. If a product requires 10 processes to produce, 10 work tasks will be generated, arranged on different production equipment, and meet the time constraints between processes. The production time system automatically calculates: task production time = takt time * quantity.
The characteristics of this example model are as follows:
1. Each product requires 2-13 processes, with large differences;
2. In all processes, the length of time varies greatly;
3. CNC machining and grinding take a long time, while other processes take a shorter time. The number and brands of equipment corresponding to the process are large;
4. In some processes, specific fixtures are required as constraints;
PlanMate scheduling example:
- Product model and process task flow: A typical process for a product is as follows:
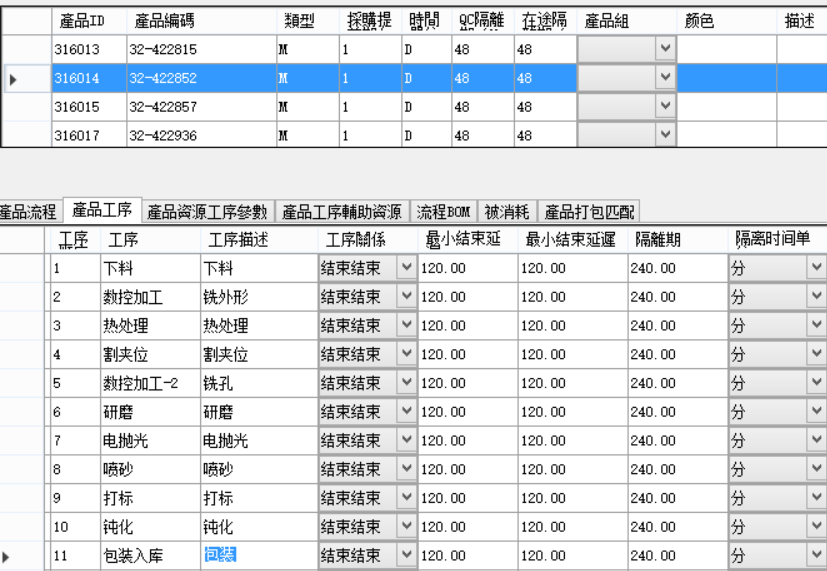
Note: The standard process name is relatively simple and needs to be accurately defined and used by the system. Users can enter process descriptions themselves and define more detailed processing details. Descriptions can be displayed in Gantt charts and appear in reports.
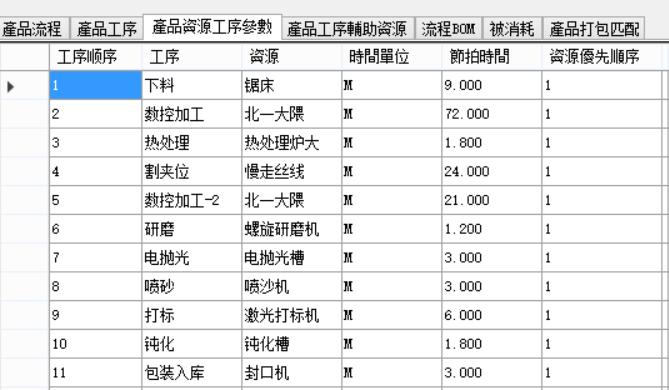
The following work orders are small and have short production times, so they are not split;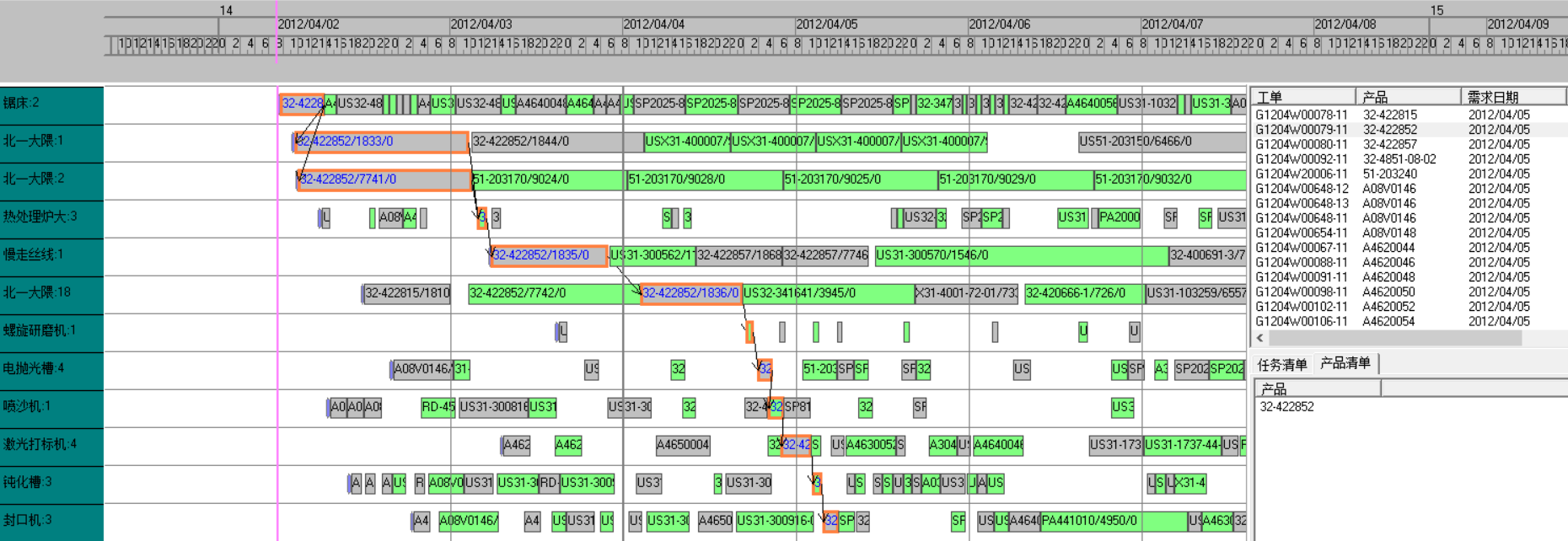
- Task splitting and auxiliary resource constraints:
The process system that requires a long processing time will automatically split it into multiple work tasks and distribute them on different equipment. The specific number of allocated devices is determined by the number of fixtures, as follows:

In the above work order schedule, CNC machining and polishing take a long time, and the system automatically dismantles the task. The length of time for splitting tasks can be defined. In this example it is defined as 22 hours.
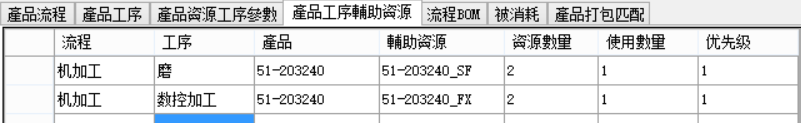
The product process model is as follows:
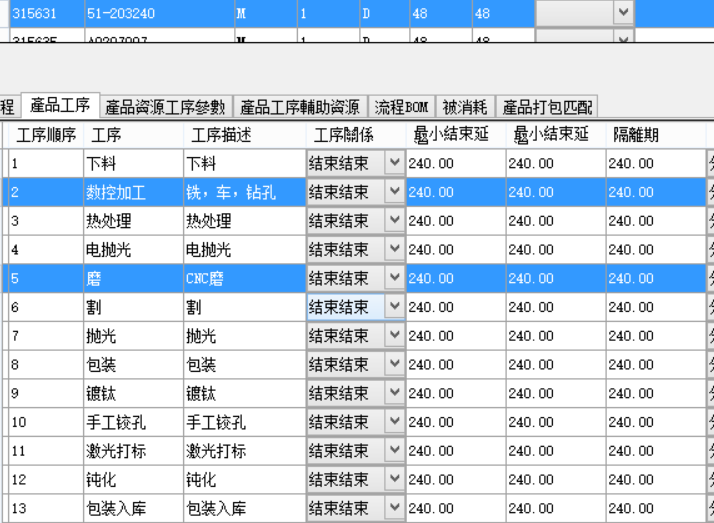
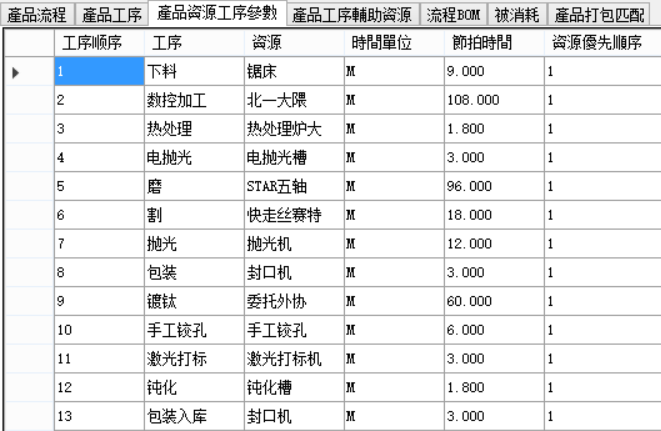
This product has defined fixtures, the quantity is 2 each, and 1 is required for production and processing. Therefore, after the task is split, it is assigned to 2 machines.
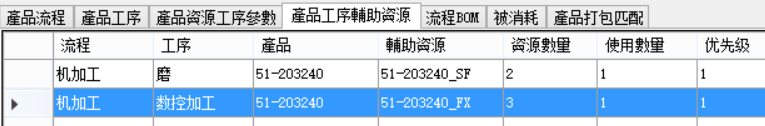
If the total number of fixtures is positioned at 3, the scheduling results are as follows:

- Multiple device selection and device load
There are many devices in the factory that are universal. For example, CNC machining equipment of different brands can complete data processing tasks but the cycle time may not. When defining the model, several more machines should be defined, and the system will balance the equipment usage.
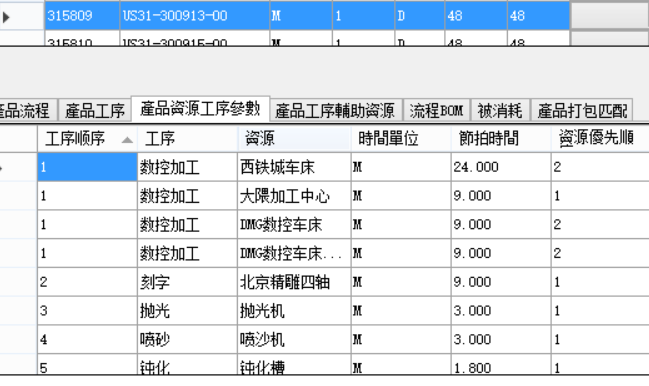
Main resources and takt time:
Auxiliary resources:
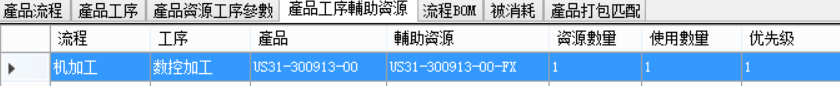
The schedule is as follows:
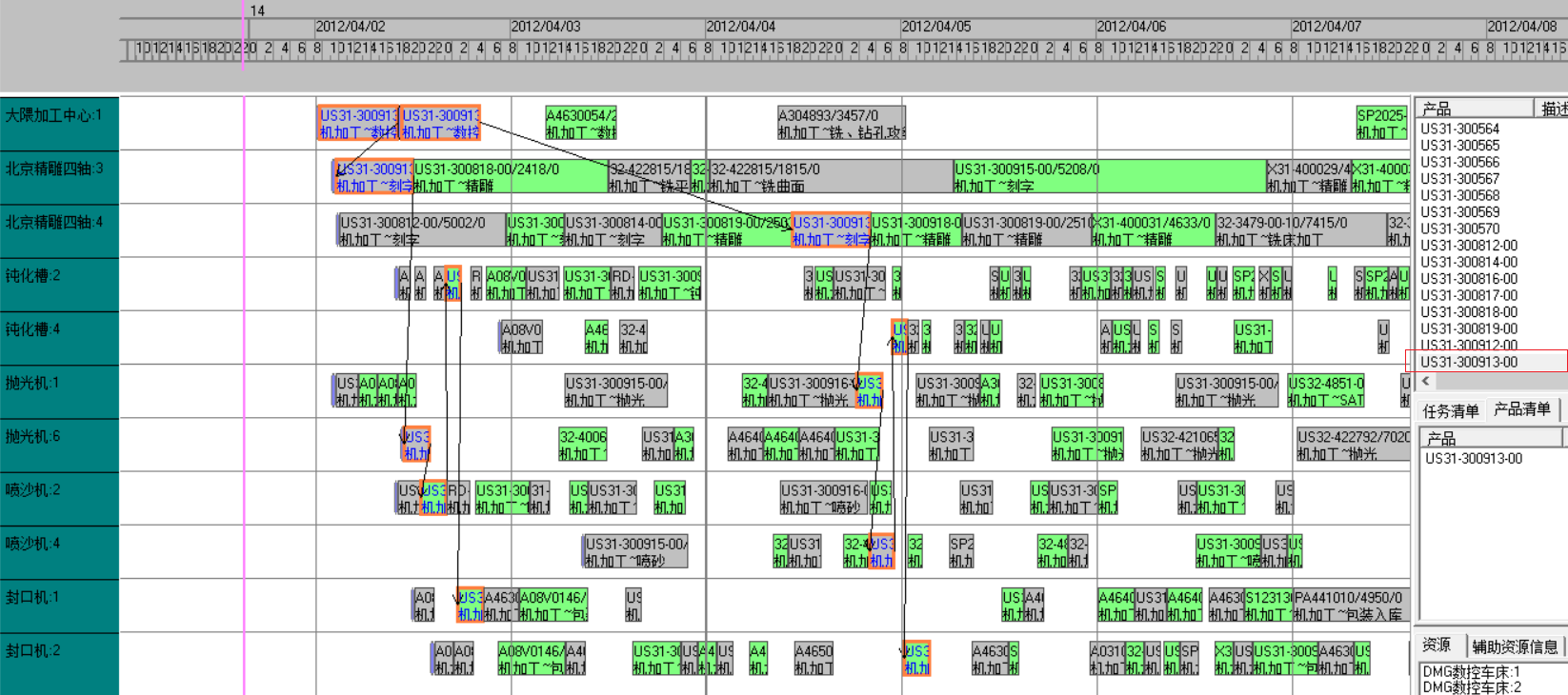
The Okuma machining center equipment is relatively empty, and the existing equipment has high priority, so the system selects this equipment for production. - System report
Equipment load rate:
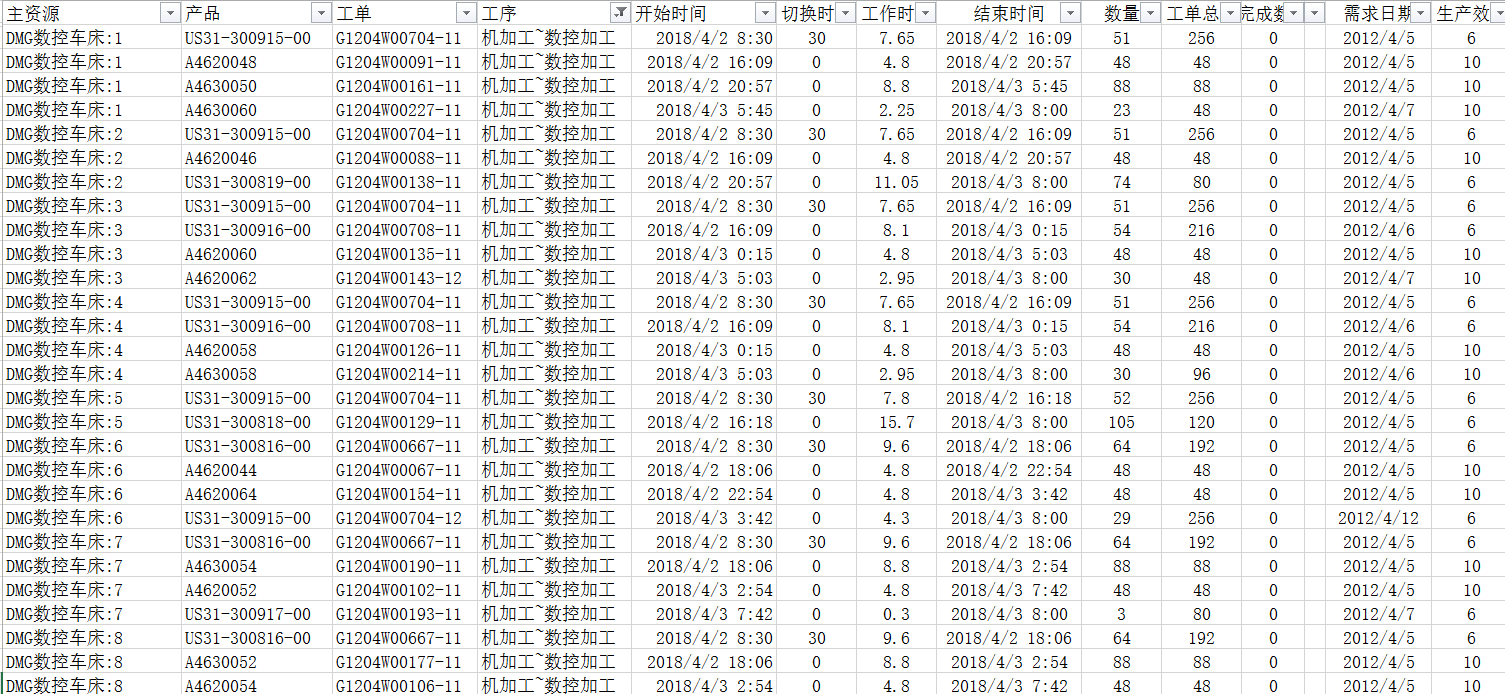
Production plan example (output to shop floor):
Example of output plan:
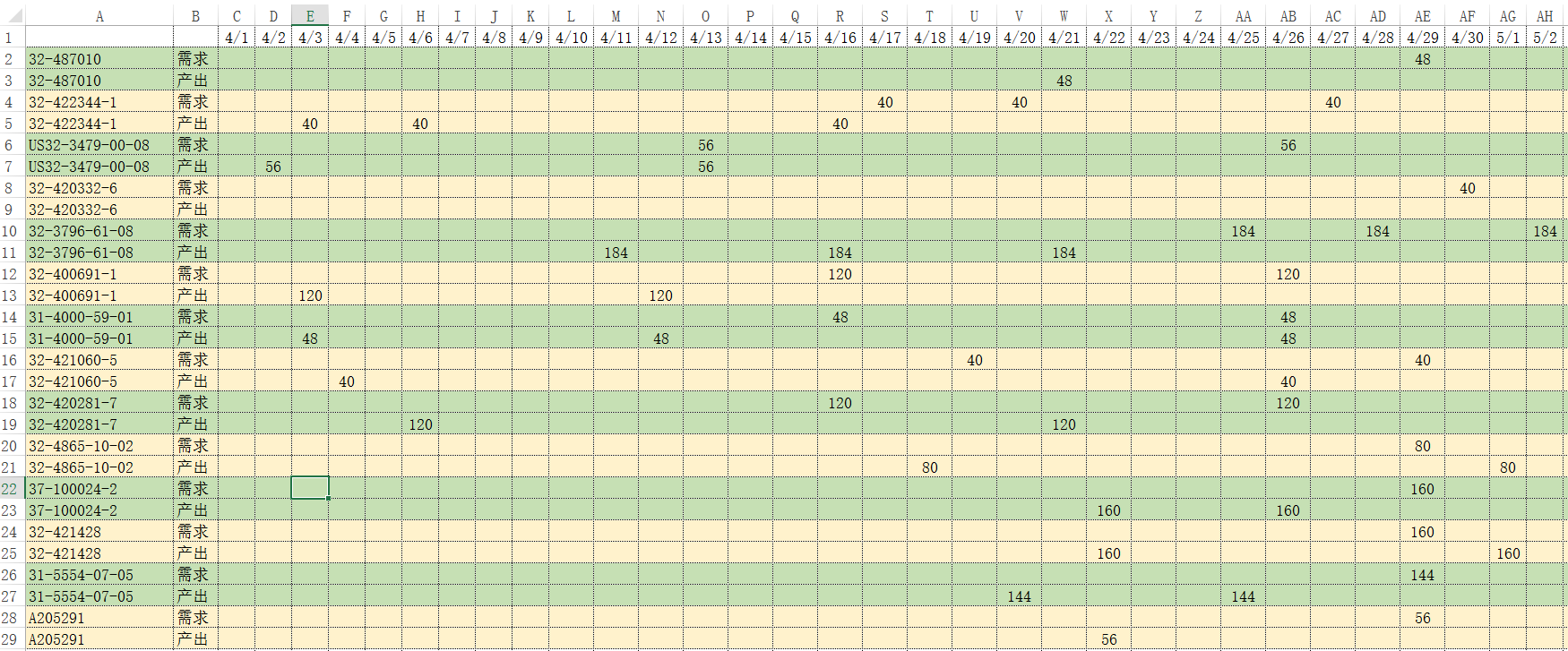
Note: The horizontal axis is the date, and the vertical axis is the product. The demand line is the order quantity of the product on this date, and the output is the quantity of the product completed on this date.
